(Bloomberg) — The financial system is getting a lift from Bidenomics and a bulging federal price range deficit, concurrently fueling hopes the US will keep away from a recession whereas fanning fears it will likely be caught with an excessive amount of debt and too-high inflation.
Most Learn from Bloomberg
A trio of laws championed by President Joe Biden – stepped-up infrastructure spending, elevated funding in a inexperienced financial system and a build-up in semiconductor manufacturing – helped provoke demand within the second quarter and is more likely to have a much bigger influence going ahead.
Financial development has additionally been unexpectedly goosed by a widening of the federal authorities’s price range deficit, pushed partially by outsized Social Safety funds and a delay in earnings tax funds by California companies and residents.
A key query is whether or not the more-than $1 trillion value of help from Bidenomics, which the president goals to make a pillar of his re-election marketing campaign, is well-timed. The controversy is whether or not it’s paving the way in which for a mushy touchdown of the financial system, or laying the groundwork for a renewed rise in inflation.
Advocates of every state of affairs discovered help for his or her views within the newest employment report. Payroll development slowed however stayed sturdy final month, buttressing hopes the US can keep away from a recession. However wage features remained elevated, feeding inflation fears.
Moody’s Analytics chief economist Mark Zandi is amongst these seeing Bidenomics as a plus, arguing it can assist offset the lagged financial influence of aggressive credit score tightening by the Federal Reserve and permit the US to skirt a recession.
“The timing may be very propitious,” he stated. He calculates that Bidenomics will make up about 0.4 share level of the comparatively meager 1% financial development fee he’s penciled in over the approaching 12 months.
Different economists fear that the Biden stimulus is working at cross functions to the Fed’s efforts to sluggish development and scale back inflation to its 2% objective — probably setting the stage for much more fee hikes subsequent 12 months.
‘Rising Threat’
“There’s a rising threat that sturdy development now fuels inflation later,” stated Neil Dutta, head of economics for Renaissance Macro Analysis, who argues a resilient financial system and sturdy labor market have already shrugged off the Fed’s rapid-fire fee will increase.
What Bloomberg Economics Says…
“If the recession we predict this 12 months is delayed relatively than averted, and the Fed finally has to hike greater than we presently anticipate — the probably perpetrator will probably be Bidenomics.”
— Anna Wong, chief US economist
To learn the complete be aware, click on right here
The Biden administration, not surprisingly, views its insurance policies as an unalloyed constructive.
“The president’s financial insurance policies, Bidenomics are working for the American folks,” Performing Labor Secretary Julie Su stated on Bloomberg Tv Friday.
So far as the general public goes, any financial features haven’t translated into elevated help for the president. Lower than 40% of registered voters gave Biden a positive ranking in a New York Instances/Siena School ballot final month.
Fed policymakers, for his or her half, have performed down the financial influence of fiscal coverage. Chair Jerome Powell stated on June 28 that it wasn’t an “essential driver” of inflation.
Advantages of Bidenomics are more and more obvious to corporations, nevertheless, with expectations of additional assist forward.
“In areas like wire and cable for telecommunications and high-voltage transmission, we’ve already seen very sturdy demand,” Dow Inc. Chief Government Officer Jim Fitterling informed analysts on July 25. “And I don’t assume that’s going to again off.”
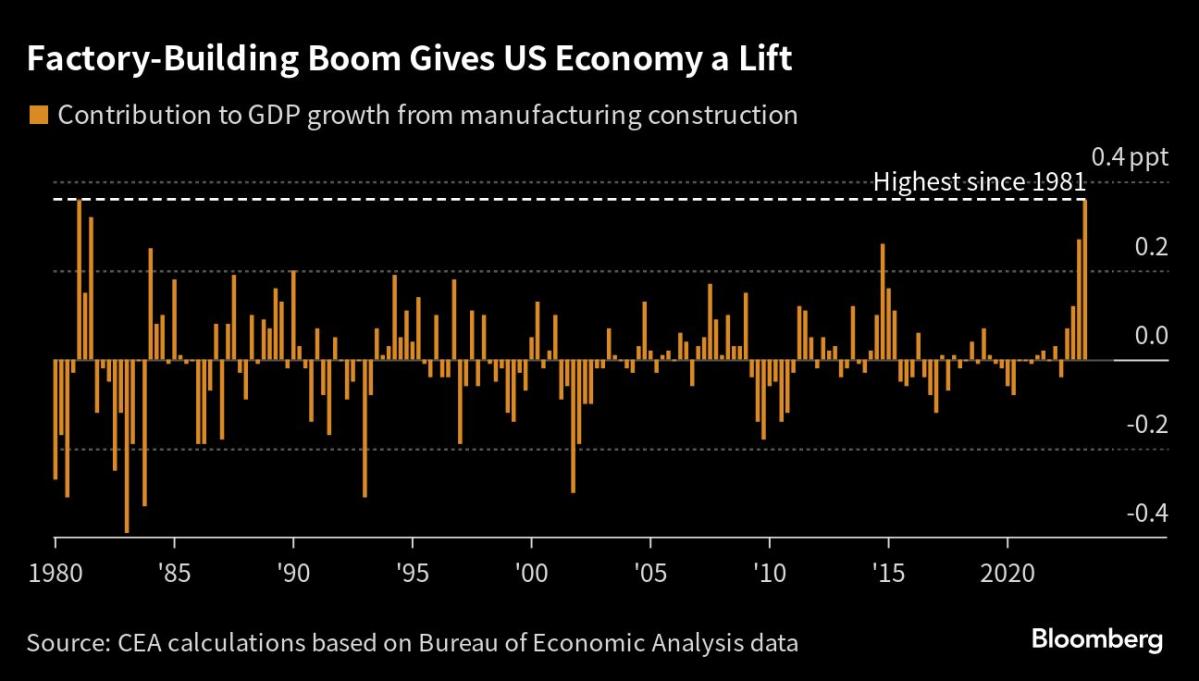
Spending on manufacturing unit development has virtually doubled previously 12 months, spurred by subsidies and different authorities help for industries like clear power and semiconductors. Enterprise giants like Ford Motor Co. and Intel Corp., together with loads of smaller corporations, are tapping the federal government packages to construct new crops.
“Corporations have been aggressively courting the federal government tax credit,” stated Anirban Basu, chief economist for the Related Builders and Contractors commerce group. “That is actually crowding in personal funding relatively than crowding it out.”
Goldman Sachs Group Inc. analysts reckon the federal government will shell out $1.2 trillion over the subsequent 10 years on tax credit and different subsidies to combat international warming beneath the Inflation Discount Act. That compares with an preliminary $391 billion price estimate by the Congressional Finances Workplace when the invoice was handed in August 2022.
Partly in response to the factory-building growth, Morgan Stanley chief US economist Ellen Zentner and her workforce lately raised their forecast for GDP development this 12 months by 0.7 share level to 1.3%, and reaffirmed their forecast of a mushy touchdown. Additionally behind the improve: elevated public infrastructure funding.
The bipartisan infrastructure invoice handed in November 2021 “is driving a growth in large-scale” tasks, the economists wrote in a July 20 report.
A few of that cash is being eaten up by a steep rise in development prices. Oregon’s transportation division, as an example, stated in February that the additional funding it was receiving from Washington for pavement restore “will largely be eroded by current inflationary tendencies.”
A scarcity of development employees is appearing to maintain prices and inflation elevated and resulting in undertaking delays, stated Basu, from the builders and contractors commerce group. Common hourly earnings amongst development employees rose 0.9% in July, and had been up 5.4% from a 12 months earlier.
Widening Deficit
The uncertainty surrounding the inflationary influence of Bidenomics is compounded by the ballooning of the price range deficit, solely a small a part of which is because of the president’s packages. For the primary 9 months of the fiscal 12 months that runs by means of September, purple ink totaled $1.4 trillion, virtually triple the year-earlier determine.
Fitch Rankings Inc. spotlighted the long-run deterioration within the authorities’s funds final week by stripping the US of its top-tier AAA credit standing.
A grab-bag of things are behind the widening of the deficit this 12 months. Some don’t have any evident influence on the financial system, reminiscent of the tip of Fed remittances to the Treasury from cash earned on its bond holdings. Others, reminiscent of a further $101 billion forked over to Social Safety recipients and a delay of California tax funds till October on account of pure disasters there, have put extra money into folks’s pockets.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. chief US economist Michael Feroli stated the larger deficit helps clarify the financial system’s shocking resilience to date this 12 months and is one cause why he’s scrapping his forecast of a recession.
However he cautioned it could be a mistake for the Fed to take the financial system’s sturdiness as a inexperienced mild to push forward with fee will increase, because the deficit is more likely to slim within the subsequent fiscal 12 months, which begins in October.
“The Fed must be cognizant of that relatively than simply going full steam forward,” he stated.
Learn Extra: JPMorgan Scraps Recession Name in Newest Signal of Rising Optimism
–With help from Hannah Pedone.
Most Learn from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2023 Bloomberg L.P.